What does my Critical Illness Cover do?
Critical Illness Cover pays you a lump sum if you’re diagnosed with a stroke, suffer a heart attack, undergo heart surgery or are diagnosed with cancer (and you don’t die within 30 days of the first diagnosis). The exact, qualifying definitions will be included in your policy wording and diagnoses must be confirmed by the appointed medical officer.
Cancer
- Any malignant solid tumour (carcinoma or sarcoma) which is microscopically characterized by uncontrolled growth of the cancer cells breaking through the basement membrane (a thin layer of tissue that covers a surface, lines a cavity, or divides a space or organ) or invading the normal surrounding tissue of origin. Borderline solid tumours, tumours considered to have a low-malignant potential, prostate and non-melanoma skin cancers are not included in this definition. For prostate cancer please see below.
- Any cancer of the blood or lymph nodes (lymphoma) treated in any of the following ways:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplant
- Maintenance biological or targeted therapy
Borderline blood or lymph node tumours are excluded from this definition.
- Prostate cancer lesions will be paid if the cancer has spread outside of the prostate gland, or if a prostatectomy has been performed, or if following a prostate biopsy there is microscopic confirmation of a prostate cancer lesion with a Gleason Score of 7 or more (a score that describes the aggressiveness of the cancer and likeliness that it will spread or progress).
Stroke
A stroke is the death or loss of functioning brain tissue as a result of a lack of blood supply. This is usually due to a blockage or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain. The stroke must have resulted in any of the following findings that are still present 30 days after the stroke and confirmed by a neurologist:
- Loss of muscle motor function (a power score of <3/5)
- Loss of speech Loss of sensation
- Loss of vision or hearing
- New diagnosis of epilepsy (recurrent fits) caused by the stroke
- Loss of function of the cerebellum (balance, co-ordination and walking difficulties)
The stroke must be visible on a brain scan (CT or MRI scan) and the area of the brain affected on the scan must correspond to the loss of brain function indicated in the list above.
Heart Surgery
Any open heart surgery (cutting through the breast bone to perform surgery to the heart) or key-hole surgery to correct (bypass) the narrowing or blockage of one or more of the heart’s (coronary) artery/ies using another artery or vein taken from elsewhere in the patient’s body.
Heart Attack
A heart attack is the death or loss of functioning heart tissue as a result of a lack of blood supply. This is usually due to a blockage of a blood vessel supplying the heart. This results in typical symptoms and can be picked up by doing an ECG (electrocardiogram) or scan of the heart and by blood tests showing a leak of heart tissue proteins or enzymes into the blood stream. Therefore, the heart attack must have resulted in all three of the following findings confirmed by a cardiologist:
- Sudden onset of symptoms in keeping with a heart attack such as chest pain AND
- Internationally recognized and documented evidence of a heart attack on the ECG (electrocardiogram) or heart imaging such as an echo done at the time of the event AND
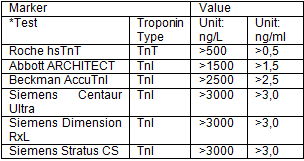
- Raised blood markers confirming the death of the heart tissue according to a troponin test result of a least five times the value of the recommended WHO (World Health Organisation) cut off level for a heart attack to have occurred as measured by a particular troponin test. This troponin level can be found on the printed laboratory result of the blood tests done at the time of the event.
Below is a table of the tests used and their qualifying levels:
*Use the relevant manufacturer’s test as it appears on the laboratory report.
What can my Critical Illness Cover be used for?
- Paying towards the costs of recuperation
- Adjusting your lifestyle to accommodate the impact of the illness
- Providing investment income for recurring expenses such as living costs
What does my Critical Illness Cover not cover?
- If you die within 30 days of the event which triggers the claim you are not covered.
- If the claimed condition is caused by intentional inhalation of fumes or intentional or negligent consumption of poisons, drugs, narcotics or medication (unless prescribed by and independent medical practitioner and used as described).
- Certain specific exclusions (which will be very clearly communicated during the process of buying a policy) based on your health or your lifestyle.
How much Critical Illness Cover can I buy?
Depending on your income, you can qualify for Critical Illness Cover of between R100 000 and R5 million.
When does my Critical Illness Cover expire?
Critical Illness expires when you turn 65 or when you die.
How can I customise my Critical Illness Cover?
You can add on to your Critical Illness Cover with our Guaranteed Insurability Benefit.
Loading